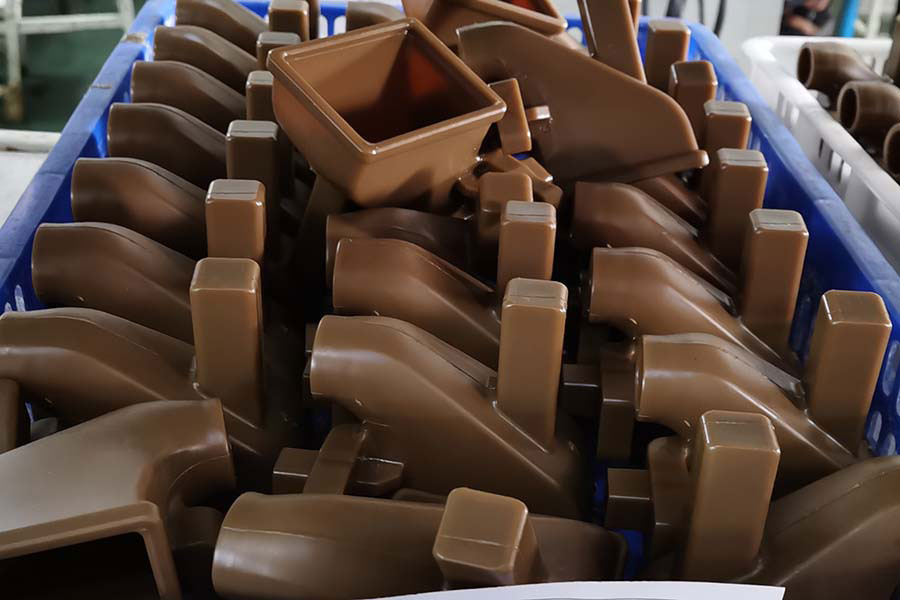
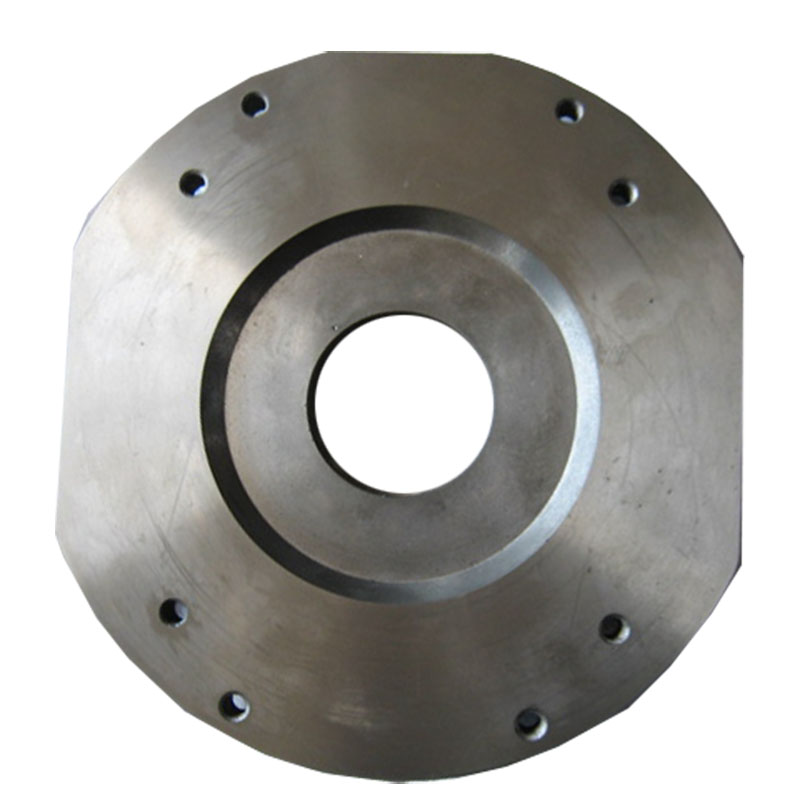
Corrosion-resistant cast steel, also called cast stainless steel, refers to alloy cast steel that exhibits strong resistance to corrosion in a variety of specific corrosive media or an environment where corrosion and mechanical factors coexist.
| Quick Views for Austenitic Stainless Steel | |
| Main Chemical Composition | Cr,Ni,C,Mo,Cu,Si,Nb,Ti |
| Performance | Non-magnetic, high toughness, high plasticity, low strength |
| Definition | Stainless steel with austenitic structure at room temperature |
| Representative Grades | 304, 316, 1.4310, 1.4301, 1.4408 |
| Machinability | Fair |
| Weldability | Generally very good |
| Typical Uses | Food machines, Hardwares, Chemical Processing...etc |
Stainless steel has a minimum chromium content of 10.5%, making it more resistant to corrosive liquid environments and to oxidation. It is highly corrosion resistant and wear resistant, provides excellent machinability, and is well-known for its aesthetic appearance. Stainless steel investment castings are "corrosion-resistant" when used in liquid environments and vapors below 1200°F (650°C) and "heat-resistant" when used above this temperature.
Austenitic stainless steel refers to stainless steel with an austenitic structure at room temperature. Austenitic stainless steel is one of the five classes of stainless steel by crystalline structure (along with ferritic, martensitic, duplex and precipitation hardened). In some areas, the austentite stainless steel is also called the 300 series stainless steel. When the steel contains about 18% Cr, 8%-25% Ni, and about 0.1% C, it has a stable austenite structure. Austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel includes the famous 18Cr-8Ni steel and the high Cr-Ni series steel developed by adding Cr and Ni content and adding Mo, Cu, Si, Nb, Ti and other elements on this basis. Austenitic stainless steel is non-magnetic and has high toughness and plasticity, but its strength is low, and it is impossible to strengthen it through phase transformation. It can only be strengthened by cold working. If elements such as S, Ca, Se, Te are added, it has good properties of machinability.
Austenitic stainless steel can also produce castings. In order to improve the fluidity of molten steel and improve casting performance, the alloy composition of cast steel should be adjusted by increasing the silicon content, enlarging the range of chromium and nickel content, and increasing the upper limit of the impurity element sulfur.
Austenitic stainless steel should be solid-solution treated before use, so as to maximize the solid solution of various precipitates such as carbides in the steel into the austenite matrix, while also homogenizing the structure and eliminating stress, so as to ensure excellent Corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. The correct solution treatment system is water cooling after heating at 1050~1150℃ (the thin parts can also be air cooled). The solution treatment temperature depends on the degree of alloying of the steel: Molybdenum-free or low-molybdenum steel grades should be lower (≤1100℃), and higher alloyed grades such as 00Cr20Ni18Mo-6CuN, 00Cr25Ni22Mo2N, etc. should be higher (1080~1150) ℃).
Austenitic 304 stainless steel steel plate, which is said to bring strong anti-rust and corrosion resistance, and has excellent plasticity and toughness, which is convenient for stamping and forming. With a density of 7.93 g/cm3, 304 stainless steel is a very common stainless steel, also known as 18/8 stainless steel in the industry. Its metal products are resistant to high temperatures and have good processing properties, so they are widely used in industry and furniture decoration industries and food and medical industries.
Equivalent Grade of Stainless Steel |
|||||||
| Categories | AISI | W-stoff | DIN | BS | SS | U.N.E. / I.H.A. | UNI |
| Martensitic and Ferritic Stainless Steel | 420 C | 1.4034 | X43Cr16 | ||||
| 440 B/1 | 1.4112 | X90 Cr Mo V18 | |||||
| - | 1.2083 | X42 Cr 13 | - | 2314 | F.5263 | - | |
| 403 | 1.4000 | X6Cr13 | 403 S 17 | 2301 | F.3110 | X6Cr13 | |
| (410S) | 1.4001 | X7 Cr 14 | (403 S17) | 2301 | F.3110 | X6Cr13 | |
| 405 | 1.4002 | X6 CrAl 13 | 405 S 17 | - | F.3111 | X6 CrAl 13 | |
| 416 | 1.4005 | X12 CrS 13 | 416 S 21 | 2380 | F.3411 | X12CrS13 | |
| 410 | 1.4006 | X 10 Cr 13 | 410 S21 | 2302 | F.3401 | X12Cr13 | |
| 430 | 1.4016 | X6 Cr 17 | 430 S 17 | 2320 | F.3113 | X8Cr17 | |
| 420 | 1.4021 | X20 Cr 13 | 420 S 37 | 2303 | F.3402 | X20Cr13 | |
| 420F | 1.4028 | X30 Cr 13 | 420 S 45 | (2304) | F.3403 | X30Cr13 | |
| (420) | 1.4031 | X39Cr13 | 420 S 45 | (2304) | F.3404 | - | |
| 431 | 1.4057 | X20 CrNi 17 2 | 431 S 29 | 2321 | F.3427 | X16CrNi16 | |
| 430F | 1.4104 | X12 CrMoS 17 | - | 2383 | F.3117 | X10CrS17 | |
| 434 | 1.4113 | X6 CrMo 17 | 434 S 17 | 2325 | - | X8CrMo17 | |
| 430Ti | 1.4510 | X6 CrTi 17 | - | - | - | X6CrTi17 | |
| 409 | 1.4512 | X5 CrTi 12 | 409 S 17 | - | - | X6CrTi12 | |
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | 304 | 1.4301 | X5 CrNi 18 9 | 304 S 15 | 2332 | F.3551 | X5CrNi18 10 |
| 305 | 1.4303 | X5 CrNi 18 12 | 305 S 19 | - | - | X8CrNi19 10 | |
| 303 | 1.4305 | X12 CrNiS 18 8 | 303 S 21 | 2346 | F.3508 | X10CrNiS 18 09 | |
| 304L | 1.4306 | X2 CrNiS 18 9 | 304 S 12 | 2352 | F.3503 | X2CrNi18 11 | |
| 301 | 1.4310 | X12 CrNi 17 7 | - | 2331 | F.3517 | X12CrNi17 07 | |
| 304 | 1.4350 | X5 CrNi 18 9 | 304 S 31 | 2332 | F.3551 | X5CrNi18 10 | |
| 304 | 1.4350 | X5 CrNi 18 9 | 304 S 31 | 2333 | F.3551 | X5CrNi18 10 | |
| 304LN | 1.4311 | X2 CrNiN 18 10 | 304 S 62 | 2371 | - | - | |
| 316 | 1.4401 | X5 CrNiMo 18 10 | 316 S 16 | 2347 | F.3543 | X5CrNiMo17 12 | |
| 316L | 1.4404 | - | 316 S 12/13/14/22/24 | 2348 | X2CrNiMo17 12 | ||
| 316LN | 1.4429 | X2 CrNiMoN 18 13 | - | 2375 | - | - | |
| 316L | 1.4435 | X2 CrNiMo 18 12 | 316 S 12/13/14/22/24 | 2353 | - | X2CrNiMo17 12 | |
| 316 | 1.4436 | - | 316 S 33 | 2343 | - | X8CrNiMo 17 13 | |
| 317L | 1.4438 | X2 CrNiMo 18 16 | 317 S 12 | 2367 | - | X2CrNiMo18 16 | |
| 329 | 1.4460 | X3 CrNiMoN 27 5 2 | - | 2324 | F.3309 | - | |
| 321 | 1.4541 | X10 CrNiTi 18 9 | 321 S 12 | 2337 | F.3553 | X6CrNiTi18 11 | |
| 347 | 1.4550 | X10 CrNiNb 18 9 | 347 S 17 | 2338 | F.3552 | X6CrNiNb18 11 | |
| 316Ti | 1.4571 | X10 CrNiMoTi 18 10 | 320 S 17 | 2350 | F.3535 | X6CrNiMoTi 17 12 | |
| 309 | 1.4828 | X15 CrNiSi 20 12 | 309 S 24 | - | - | X16 CrNi 24 14 | |
| 330 | 1.4864 | X12 NiCrSi 36 16 | - | - | - | - | |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | S32750 | 1.4410 | X 2 CrNiMoN 25 7 4 | - | 2328 | - | - |
| S31500 | 1.4417 | X 2 CrNiMoSi 19 5 | - | 2376 | - | - | |
| S31803 | 1.4462 | X 2 CrNiMoN 22 5 3 | - | 2377 | - | - | |
| S32760 | 1.4501 | X 3 CrNiMoN 25 7 | - | - | - | - | |
| 630 | 1.4542 | X5CrNiCNb16-4 | - | - | - | - | |
| A564/630 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
Ferrous and Non-ferrous Materials for Investment Casting, Lost Wax Casting Process:
- • Gray Iron: HT150, HT200, HT250, HT300, HT350; GJL-100, GJL-150, GJL-200, GJL-250, GJL-300, GJL-350; GG10~GG40.
- • Ductile Iron or Nodular Iron: GGG40, GGG50, GGG60, GGG70, GGG80; GJS-400-18, GJS-40-15, GJS-450-10, GJS-500-7, GJS-600-3, GJS-700-2, GJS-800-2; QT400-18, QT450-10, QT500-7, QT600-3, QT700-2, QT800-2;
- • Carbon Steel: AISI 1020 - AISI 1060, C30, C40, C45.
- • Steel Alloys: ZG20SiMn, ZG30SiMn, ZG30CrMo, ZG35CrMo, ZG35SiMn, ZG35CrMnSi, ZG40Mn, ZG40Cr, ZG42Cr, ZG42CrMo...etc on request.
- • Stainless Steel: AISI 304, AISI 304L, AISI 316, AISI 316L, 1.4401, 1.4301, 1.4305, 1.4307, 1.4404, 1.4571 and other stainless steel grade.
- • Brass, Red Copper, Bronze or other Copper-based alloy metals: ZCuZn39Pb3, ZCuZn39Pb2, ZCuZn38Mn2Pb2, ZCuZn40Pb2, ZCuZn16Si4
- • Other Materials as per your unique requirements or according to ASTM, SAE, AISI, ACI, DIN, EN, ISO, and GB standards
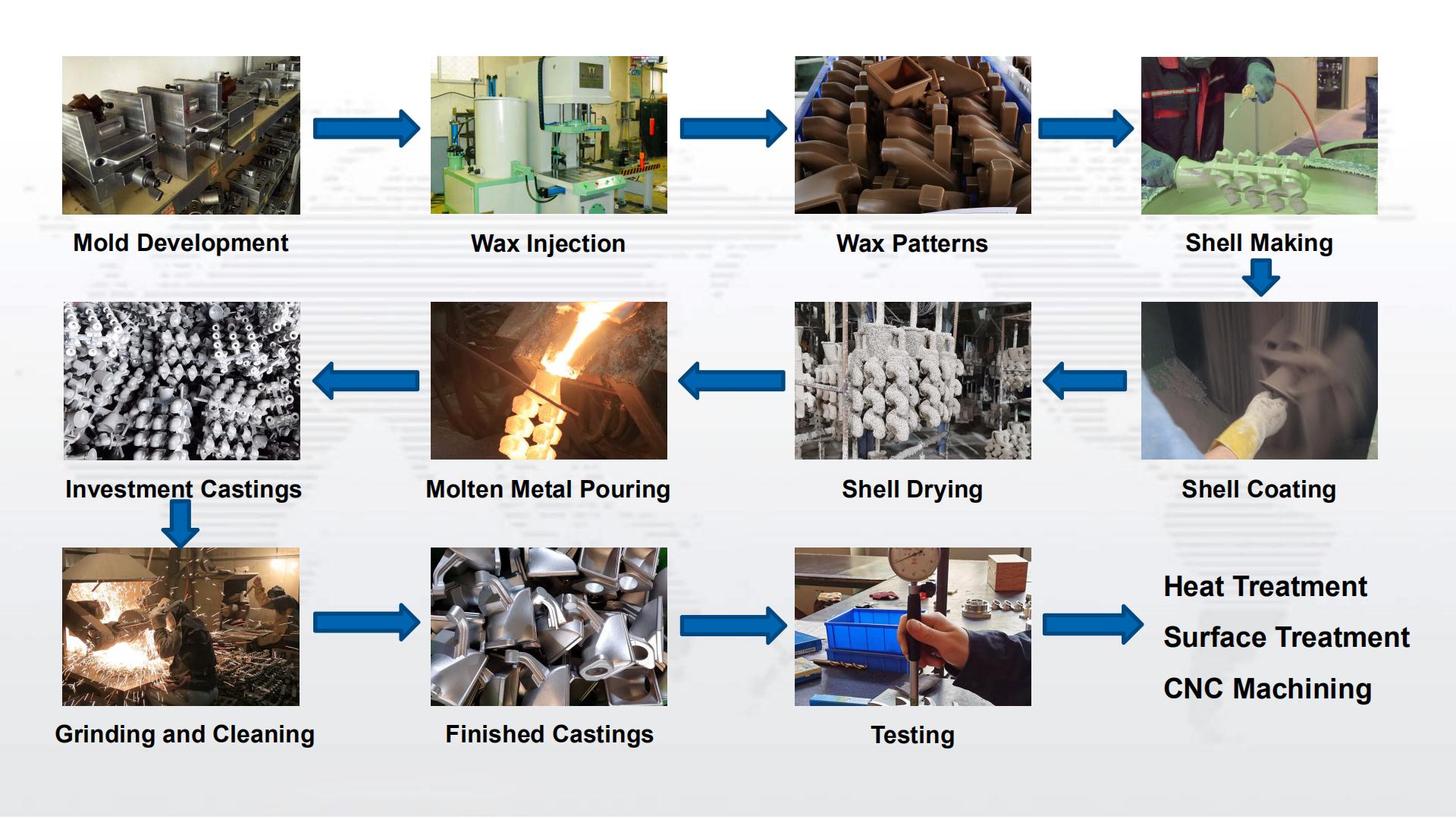
The steps involved in the process or the lost wax casting are:
- • Create a wax pattern or replica
- • Sprue the wax pattern
- • Invest the wax pattern
- • Eliminate the wax pattern by burning it (inside the furnace or in hot water) to create a mould.
- • Force molten metal pour into the mould
- • Cooling and Solidification
- • Remove sprue from the castings
- • Finish and polish the finished investment castings
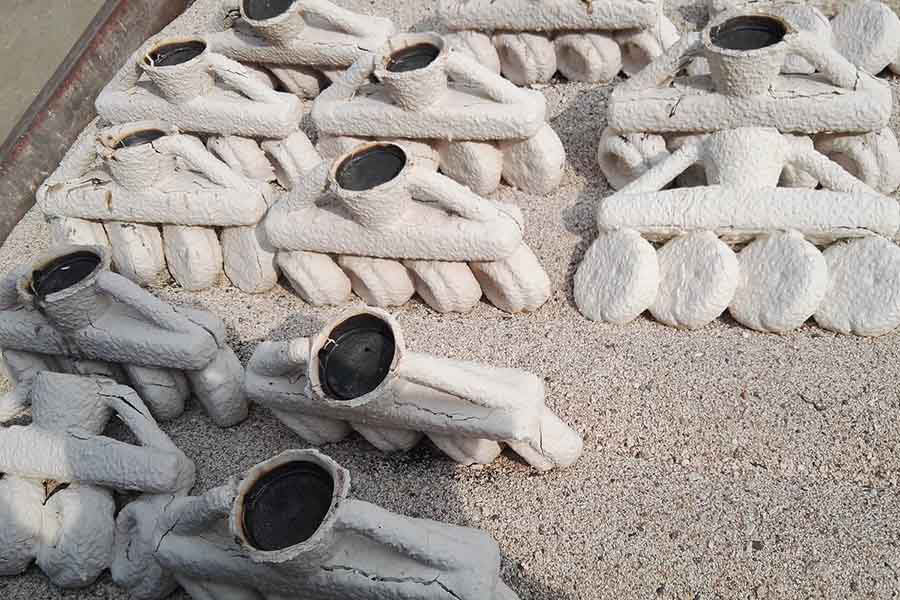




Heat Treatment of AISI 316 Stainless Steel Castings:
Heat to 1900°F (1040°C) minimum, holding for sufficient time, quench in water or rapid cool by other means. AISI 316 equal to CF8M/F316 and Chinese Standard 0Cr17Ni12Mo2. AISI 314 is a molybdenum bearing modification of AISI 304 alloy and is the cast equivalent of wrought CF8M Stainless steel. The presence of molybdenum increases the general corrosion resistance and the resistance to pitting by chlorides. The alloy is used in mildly acidic and alkaline conditions and for handling citric, oxalic and phosphoric acids.