-

Ferritic Stainless Steel Casting
Ferritic stainless steel refers to stainless steel with body-centered cubic ferrite as the matrix structure at high temperature and normal temperature. Ferritic stainless steel has iron and chromium as the main elements, generally does not contain nickel, and some contai...Read more -
Magnetic Particle Inspection of Casting Internal Defects
Magnetic particle inspection is a detection method that uses the properties of ferromagnetic materials (such as steel, iron, cobalt, nickel, etc.) to be magnetized. When the metal casting is strongly magnetized by the magnetic field, if there is a defect perpendicular to...Read more -

304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is a grade of stainless steel produced according to the American ASTM standard. Among all stainless steel materials, 304 stainless steel is almost the most common grade. The density of 304 stainless steel is 7.93 g/cm³. The professional name of 304 st...Read more -

China Material Grades for Grey Iron and Ductile Iron
Cast iron is an iron-carbon alloy with a mass fraction of carbon greater than 2.11%. Cast iron is obtained by remelting pig iron in the furnace, adding ferroalloy, scrap steel, and returning to the furnace to adjust the composition. Grey cast iron and ductile iron are th...Read more -
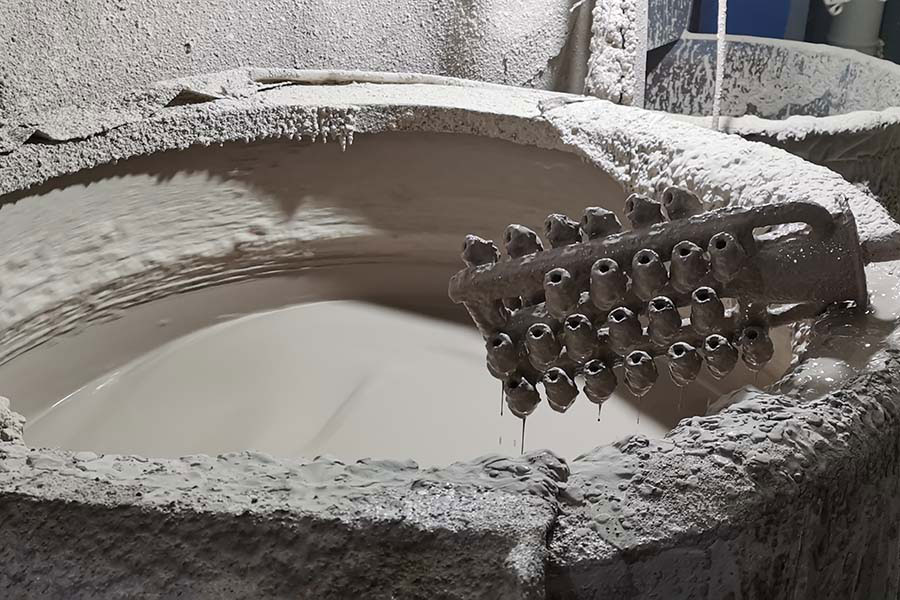

Silica Sol Binder In Investment Casting
The choice of silica sol coating will directly affect the surface roughness and dimensional accuracy of investment castings. Silica sol coatings generally can directly select silica sol with a mass fraction of silica of 30%. The coating process is simple and the operatio...Read more -
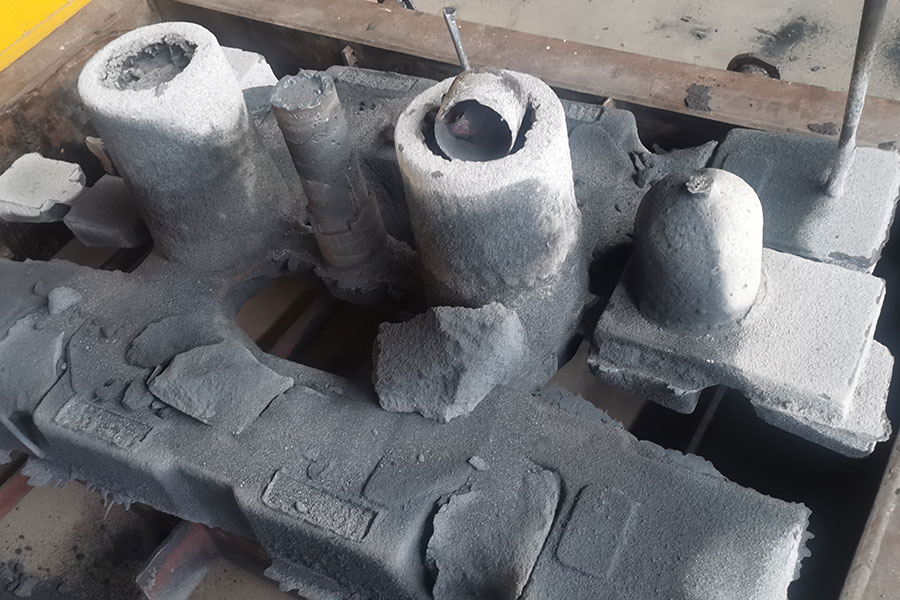

Chills for Metal Casting
Chill is the chilled material placed inside the cavity, the surface of the cavity and the inside of the mold in order to speed up the local cooling rate of the casting. The chills are used in conjunction with the gating system and the riser system to control the solidifi...Read more -
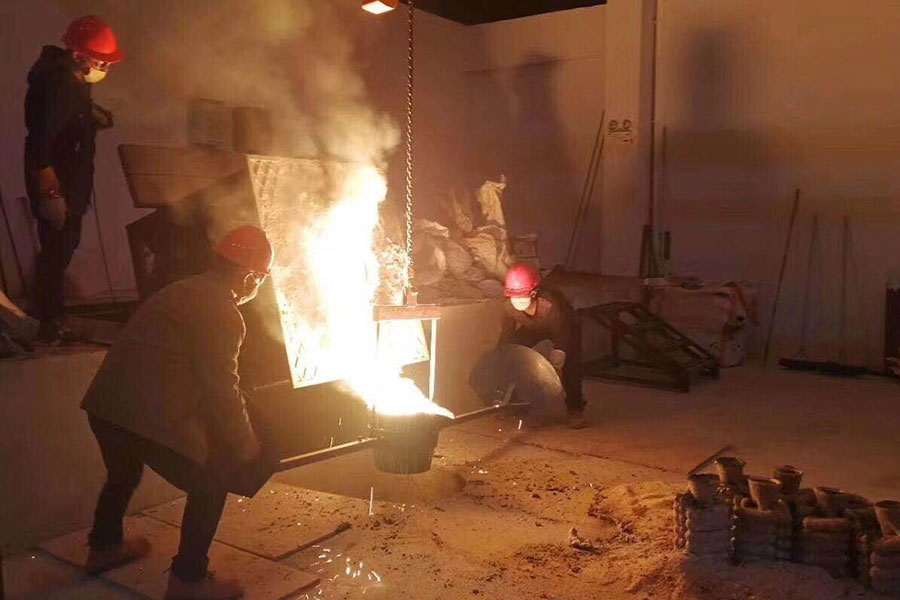

Precision Casting for Stainless Steel Castings
Precision casting is also called investment casting. This casting process minimizes or does not cut during the casting process. It is a casting method with a wide range of applications, high dimensional accuracy of the casting, and excellent surface quality. It is not in...Read more -
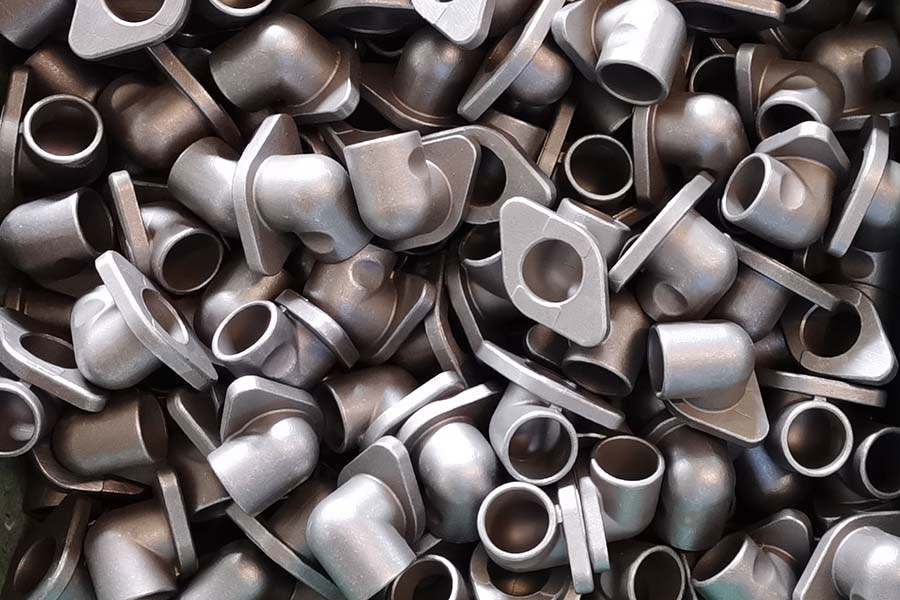

Surface Treatment of Metal Casting Parts
Metal surface treatment is a process of artificially forming a surface layer on the surface of a metal base material that is different from the mechanical, physical and chemical properties of the base. The purpose of surface treatment is to meet the product's corrosion r...Read more -
Heat Treatment of Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel Castings
Precipitation hardening (PH) martensitic stainless steel generally contains alloying elements such as copper, lead, molybdenum, and titanium that form a hardened phase. These alloying elements have greater solubility in austenite, but very little in martensite. Therefore...Read more -

Heat Treatment of Austenitic Stainless Steel Castings
The as-cast structure of austenitic stainless steel castings is austenite + carbide or austenite + ferrite. Heat treatment can improve the corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel castings. Equivalent Grade of Austenitic Stainless Steel AISI ...Read more -

Heat Treatment of Martensitic Stainless Steel Castings
Martensitic stainless steel refers to a type of stainless steel whose microstructure is mainly martensite. The chromium content of martensitic stainless steel is in the range of 12% - 18%, and its main alloying elements are iron, chromium, nickel and carbon. Martensitic ...Read more -

Heat Treatment of Wear (Abrasion) Resistant Steel Castings
Wear-resistant (or abrasion-resistant) cast steel refers to cast steel with good wear resistance. According to chemical composition, it is divided into non-alloy, low-alloy and alloy wear-resistant cast steel. There are many types of wear-resistant steel, which can be ro...Read more













