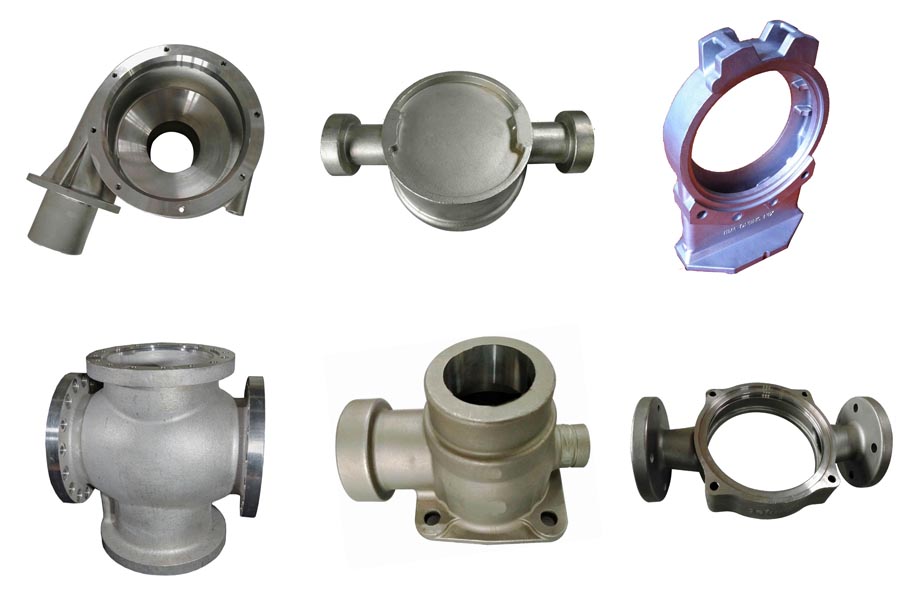
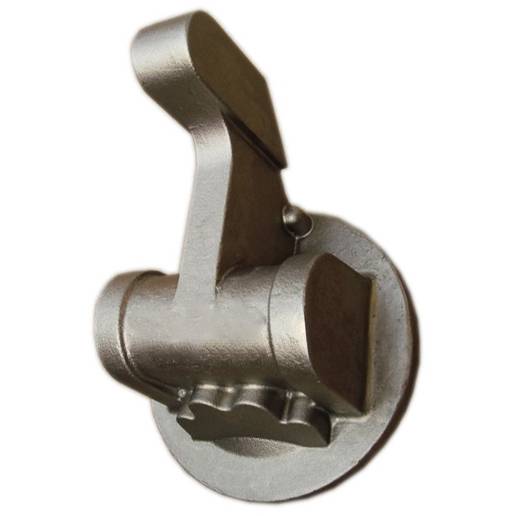
According to the level of carbon content, carbon steel for casting is generally divided into low carbon steel, medium carbon steel and high carbon steel. The cast carbon steels of all countries in the world are generally classified according to their strength, and corresponding grades are formulated.
Regarding the chemical composition of carbon steel, except for phosphorus and sulfur, there are no restrictions or only upper limits on other chemical elements. Under the above premise, the chemical composition of cast carbon steel is determined by the foundry according to the required mechanical properties.
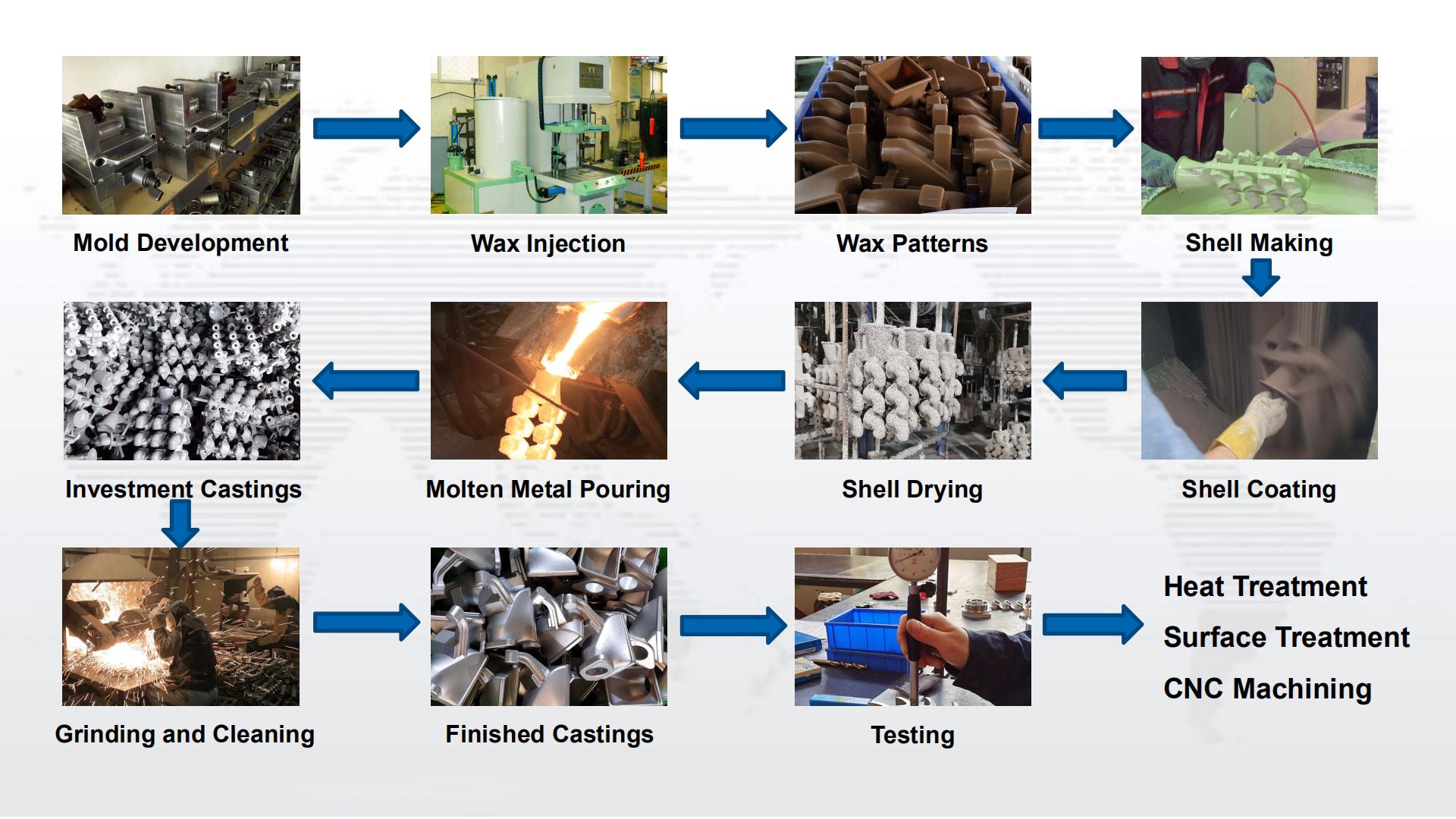
The heat treatment methods of carbon steel castings are usually annealing, normalizing or normalizing + tempering. For some high carbon steel castings, quenching and tempering can also be used, that is, quenching + high temperature tempering, so as to improve the comprehensive mechanical properties of carbon steel castings. Small carbon steel castings can be directly quenched and tempered from the as-cast state. For large-scale or complex-shaped carbon steel castings, it is appropriate to perform quenching and tempering treatment after normalizing treatment.
The effect of carbon on the microstructure and properties of carbon steel
1) The influence of carbon on the structure of carbon steel
Carbon is the main element that determines the metallographic structure and properties of steel. In the range of hypoeutectoid steel, as the carbon content increases, the relative amount of ferrite decreases and the relative amount of pearlite increases. When reaching the eutectoid composition, all are pearlite. In the hypereutectoid range, as the carbon content increases, the relative amount of proeutectoid cementite increases and the relative amount of pearlite decreases.
2) The effect of carbon on the mechanical properties of carbon steel
Carbon affects the mechanical properties of carbon steel by affecting the relative amounts and distribution characteristics of each structural component in the microstructure. In general, as the carbon content increases, the hardness of carbon steel will increase, but its impact energy and elongation will decrease. The tensile strength and yield strength will first increase and then decrease as the carbon content in carbon steel increases.
3) The effect of carbon on the cutting performance of carbon steel castings
Low-carbon steel has a large amount of ferrite, low hardness, good plasticity, and easy sticking, so its cutting performance is relatively poor. There are more cementite in high carbon steel. When the cementite is distributed in flake and network, the tool is easy to wear, so its cutting performance is relatively poor. The ratio of ferrite and cementite in medium carbon steel is appropriate, hardness and plasticity are also moderate, and the cutting performance is better. The cutting performance is the best when the hardness range of steel castings is 180-230 HBW.
4) The influence of carbon on the casting performance of carbon steel
At the same temperature, the fluidity of molten steel with different carbon content is different. Because steels with different carbon content have different degrees of development in dendrites. The greater the temperature interval of the crystallization zone (the temperature difference between the liquidus line and the solidus line), the more developed the dendritic crystals of the carbon steel, that is, the worse the fluidity of the molten steel, which results in the ability of the molten steel to fill the mold.